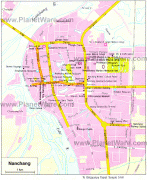
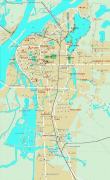
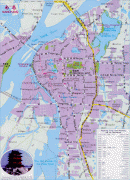
Nanchang
As the Nanchang Uprising in 1927 is distinctively recognized by the ruling Communist Party as "firing the first gunshot against the evil Nationalists", the current government has therefore named the city since 1949 "the City of Heroes", "the place where the People's Liberation Army was born", and the most widely known "place where the military banner of the People's Liberation Army was first raised". Nanchang is also a major city, appearing among the top 150 cities in the world by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index and home to Nanchang University, the key national university of “Project 211” in the city.
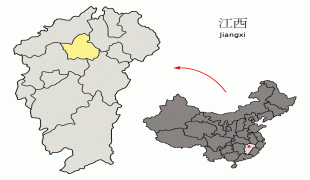
The territories encompassing modern-day Jiangxi Province—including Nanchang—was first incorporated into China during the Qin dynasty, when it was conquered from the Baiyue peoples and organized as Jiujiang Commandery. In 201 BC, during the Han dynasty, the city was given the Chinese name Nanchang and became the administrative seat of Yuzhang Commandery, and was governed by Guan Ying, one of Emperor Gaozu of Han's generals. The name Nanchang means "southern flourishing", derived from a motto of developing what is now southern China that is traditionally attributed to Emperor Gaozu himself.
In AD 589, during the Sui dynasty, this commandery was changed into a prefecture named Hongzhou, and after 763 it became the provincial center of Jiangxi, which was then beginning the rapid growth that by the 12th century made it the most populous province in China.
In 653 the Tengwang Pavilion was constructed, and in 675 Wang Bo wrote the classic "Tengwang Ge Xu", a poetic introductory masterpiece celebrating the building, making the building, the city, and the author himself known to literate Chinese-speaking population ever since. The Pavilion has been destroyed and rebuilt several times throughout history. Its present form was reconstructed in the 1980s after being destroyed in 1929 during the Chinese Civil War.
In 959, under the Southern Tang regime, Nanchang was made superior prefecture and the southern capital. After the conquest by the Song regime in 981 it was reverted to the name Hongzhou. In 1164 it was renamed Longxing prefecture, which name it retained until 1368. During the Yuan dynasty it was the capital of Jiangxi Province, an area that included Guangdong as well. At the end of the Yuan (Mongol) period (1279–1368), it became a battleground between Zhu Yuanzhang, the founder of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644), and the rival local warlord, Chen Youliang. At the beginning of the 16th century it was the power base from which Zhu Chenhao, the Prince of Ning, launched a rebellion against the emperor.
During the Yuan Dynasty, it might have been the centre of porcelain trade
During the reign of the Wanli Emperor of the Ming dynasty, it housed relatives of the emperor who had been exiled because they were potential claimants of the imperial throne, members of the imperial family constituting about one quarter of the city's population; as a result of this, Matteo Ricci came here when trying to gain entry to Beijing.
In the 1850s it suffered considerably as a result of the Taiping Rebellion (1850–64), and its importance as a commercial centre declined as the overland routes to Canton were replaced by coastal steamship services in the latter half of the 19th century. Nanchang has, however, remained the undisputed regional metropolis of Jiangxi.
On August 1, 1927, Nanchang was the site of one of a series of insurrections organized by the communists. The Nanchang Uprising, led by pro-communist Kuomintang officers under Soviet direction, succeeded in holding the city for only a few days, and provided a core of troops and a method of organization from which the People's Liberation Army (PLA) later developed.
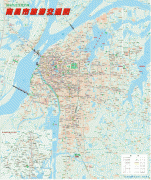
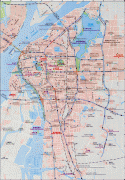
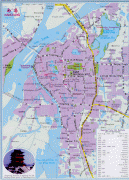
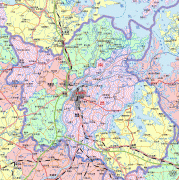
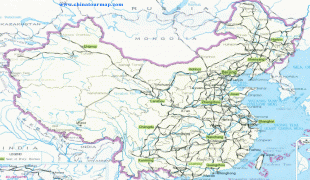
Map - Nanchang
Map
Country - China
 |
 |
| Flag of China | |
Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dynasties. Chinese writing, Chinese classic literature, and the Hundred Schools of Thought emerged during this period and influenced China and its neighbors for centuries to come. In the third century BCE, Qin's wars of unification created the first Chinese empire, the short-lived Qin dynasty. The Qin was followed by the more stable Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), which established a model for nearly two millennia in which the Chinese empire was one of the world's foremost economic powers. The empire expanded, fractured, and reunified; was conquered and reestablished; absorbed foreign religions and ideas; and made world-leading scientific advances, such as the Four Great Inventions: gunpowder, paper, the compass, and printing. After centuries of disunity following the fall of the Han, the Sui (581–618) and Tang (618–907) dynasties reunified the empire. The multi-ethnic Tang welcomed foreign trade and culture that came over the Silk Road and adapted Buddhism to Chinese needs. The early modern Song dynasty (960–1279) became increasingly urban and commercial. The civilian scholar-officials or literati used the examination system and the doctrines of Neo-Confucianism to replace the military aristocrats of earlier dynasties. The Mongol invasion established the Yuan dynasty in 1279, but the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) re-established Han Chinese control. The Manchu-led Qing dynasty nearly doubled the empire's territory and established a multi-ethnic state that was the basis of the modern Chinese nation, but suffered heavy losses to foreign imperialism in the 19th century.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNY | Renminbi | ¥ or 元 | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ZH | Chinese language |
| UG | Uighur language |
| ZA | Zhuang language |